Mapping PCC Rules into Session Rules: Policy Application in 5G Networks
Note
Author: Alonza Tu
Date: 2024/11/13
Roles of PCC Rules and Session Rules
In 5G networks, managing service quality for diverse applications is critical to providing users with a consistent experience. PCC, which stands for Policy and Charging Control, rules play a central role in regulating traffic flows, enforcing quality standards, and adapting network resources according to real-time conditions.
Session Rules serve as the operational framework for implementing PCC decisions at the user session level. They are responsible for managing session establishment, maintenance, and termination while ensuring proper resource allocation and QoS enforcement. These rules translate high-level policy decisions into concrete network behaviors, coordinating between different network functions to maintain service quality and optimize resource utilization throughout the session lifecycle.
Abstract of Network Functions
- PCF(Policy Control Function): The PCF is responsible for generating PCC rules based on the service requirements and network conditions.
- SMF(Session Management Function): The SMF is responsible for translating PCC rules received from the PCF into actionable configurations on the user plane.
- UPF(User Plane Function): The UPF enforces the PDRs based on the rules set by SMF.
- UE(User Equipment): The UE is the terminal equipment that connects to the network and communicates with the core network.
Process of Mapping PCC Rules into Session Rules
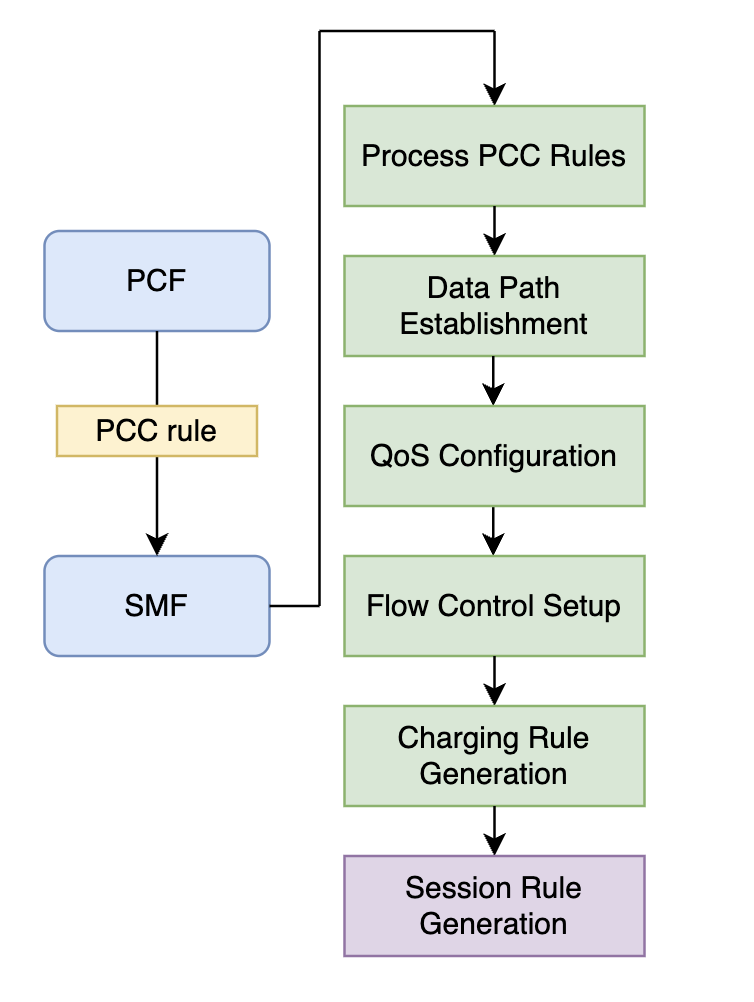
-
PCF transmits PCC rules to SMF.
- PCF transmits SmPolicyDecision to SMF, which contains:
- PCC rules: PCC rules specify how traffic should be handled based on various conditions, including data volume, priority, and the quality of service (QoS) requirements.
- QoS decision: The Quality of Service (QoS) decision specifies the level of service quality that should be applied to a particular network session. This includes parameters like latency, data rate, and packet loss, which collectively determine how reliably and quickly data is transmitted.
- Flow control decision: Flow control decisions determine how network traffic is regulated to prevent congestion, ensuring a smooth flow of data. It is essential to maintaining overall network stability and user experience.
- Charging decision: The charging decision outlines how usage fees are calculated for the services consumed by the user. It specifies which traffic should be charged and under what conditions, as well as the applicable rates.
- PCF transmits SmPolicyDecision to SMF, which contains:
-
SMF processes PCC rules.
- After receiving the SmPolicyDecision, SMF will use
ApplyPccRules()to translate PCC rules into session rules. - It includes three main steps:
- Create or update the data path for each PCC rule.
- Process relative QoS, flow control, and charging rules' parameters.
- After receiving the SmPolicyDecision, SMF will use
-
Data path establishment.
- In the beginning of
CreatePccRuleDataPath(), it will get routing position message from tcData(i.e., traffic control data), including DNAI(i.e., data network access identifier). - Next, SMF will configure the UPF selection parameters which contains DNN, network slice and DNAI information and use these parameters to create the user plane data path.
- Then, check whether it is no default path and PCC priority is 255, if so, it will set this path as the default data path.
- Also, it will set if this flow is GBR(i.e., guaranteed bit rate) flow or not, as well as activate the tunnel and PDR according to the priority.
- Before returning, it will setup the PCC parameters, add charging rule(including
chgLevelandchgData) and configure the QoS(includingQFIandqosData) for later use.
- In the beginning of
-
QoS configuration.
- In this step, SMF will assign a unique QFI via
AssignQFI()to each PCC rule and use this QFI to configure the QoS flow and data path according to the QoS data. - In
AddQoS(), it is designed to add Quality of Service (QoS) configurations for a given session, based on the QoS parameters and a specific QoS Flow Identifier (QFI). Here’s a breakdown of what this function does:- Default QFI check: If the QoS parameter is nil and the QFI is not 1 (which is treated as the default QFI), the function will return immediately, implying that no additional QoS setup is required for non-default QFIs when QoS is missing.
- Iterate Over Data Path Nodes: The function iterates through each data path node, starting from
FirstDPNodeand moving through each node in sequence. - QER(QoS Enforcement Rule) Management: For each node, it fetches the UUID of the UPF (User Plane Function) node and creates a unique QoS ID based on the UUID and qfi. If a QER entry does not already exist for the given QoS ID in the session context (
smContext.QerUpfMap), a new QER is created and configured. - QER Setup: The QER includes the QFI value and opens both uplink and downlink gates to allow traffic in both directions.
- QER Linking: Once the QER is configured, the function links it to the PDRs (Packet Detection Rules) in the uplink and downlink tunnels of the node, if they exist. This ensures that the QER settings are applied to data packets as they traverse the UPF.
- In this step, SMF will assign a unique QFI via
-
Flow control setup.
- In
ActivateTunnelAndPDR(), we will use tunnel and PDR to setup the flow forward rule through these steps:- Activating Tunnels: It iterates through all DP Nodes(Data Path Nodes) in the given DataPath and activates both uplink and downlink tunnels for each node.
- Setting Up URR (Optional): Depending on the configuration in
smContext, it may add a URR(Usage Reporting Rule) to monitor traffic and usage on the data path. - Activating PDR: It then configures PDRs for each DP Node. For each node, the function:
- Sets up QERs for managing data rates.
- Configures FARs(Forwarding Action Rules) for traffic forwarding, including outer header creation where necessary.
- Configures Uplink and Downlink PDRs: For each DP Node, it establishes the uplink and downlink PDRs, defining parameters such as interface information, IP addresses, and header removal options.
- In
-
Charging rule generation.
- Before we add the actual charging rule, we need to call
IdentifyChargingLevel()to identify the charging level is PDU session level or flow level. Then, we will add charging rule viaAddChargingRules():- Iterating through DP Nodes: For each node in the DataPath, if the node is an anchor UPF, the function proceeds with setting up charging rules.
- Charging Info and URR ID Allocation:
- Creates a ChargingInfo structure containing the rating group, charging level, and UPF ID.
- Allocates a unique URR ID using UrrIDGenerator. If this allocation fails, an error is logged and the function returns.
- URR Setup:
- It builds an ID key to map this URR to the UPF node.
- Checks if the URR already exists in smContext.UrrUpfMap:
- Online Charging:
- Creates a URR with a start trigger to detect the beginning of the Service Data Flow (SDF).
- Sets the ChargingMethod to ONLINE_CHARGING.
- Offline Charging:
- Configures URR reporting based on a volume threshold (e.g., data usage).
- Sets the ChargingMethod to OFFLINE_CHARGING.
- Online Charging:
- If the URR is new, it is added to smContext.UrrUpfMap.
- Before we add the actual charging rule, we need to call
-
Session rule generation.
- After finishing the above steps, SMF will generate the session rule by calling
ApplySessiongRules().
- After finishing the above steps, SMF will generate the session rule by calling
Conclusion
The mapping of PCC rules into session rules is a critical process in 5G networks, ensuring that high-level policy decisions are effectively translated into concrete network behaviors. This process involves collaboration between the PCF, SMF, UPF, and UE, coordinating between different network functions to maintain service quality and optimize resource utilization throughout the session lifecycle.
Reference
- TS 23.502
- TS 23.503
- TechSpec 23.501 5.7 QoS Model
- Introduction to 5G Quality of Service (QoS)
- 核心網路的策略與計費
About
Hello, I'm Alonza. This autumn, I’m excited to be joining the free5GC project with a lot of enthusiasm. I look forward to diving into the technical aspects of the 5G core network and growing my expertise in this cutting-edge field. My goal is to learn alongside the team, contribute meaningfully, and help advance the development of 5G technology together.
Connect with Me
- GitHub: https://github.com/Alonza0314
- Website: Alonza0314